Gout
- Created in Ball/Joint/Tendon
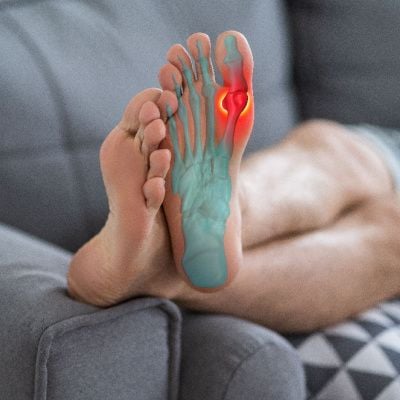 Gout, often characterized by sudden and intense joint pain, is a form of inflammatory arthritis caused by the accumulation of uric acid crystals in the joints. This condition, while historically associated with indulgence in rich foods and alcohol, can affect anyone and requires careful management. In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the intricacies of gout, exploring its causes, symptoms, diagnostic approaches, and effective treatment strategies. Additionally, we'll discuss lifestyle modifications to help individuals better manage and prevent gout flare-ups.
Gout, often characterized by sudden and intense joint pain, is a form of inflammatory arthritis caused by the accumulation of uric acid crystals in the joints. This condition, while historically associated with indulgence in rich foods and alcohol, can affect anyone and requires careful management. In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the intricacies of gout, exploring its causes, symptoms, diagnostic approaches, and effective treatment strategies. Additionally, we'll discuss lifestyle modifications to help individuals better manage and prevent gout flare-ups.
Understanding Gout
What is Gout?
Gout is a type of arthritis that results from the buildup of uric acid in the bloodstream, leading to the formation of needle-like crystals in the joints. These crystals trigger inflammatory responses, causing severe pain, swelling, and redness in the affected joints. The big toe is a common site of gout attacks, but it can also affect other joints such as the ankles, knees, elbows, wrists, and fingers.
Causes of Gout
- Uric Acid Buildup: Gout occurs when there is an excess of uric acid in the blood, leading to the formation of crystals in the joints.
- Dietary Factors: Consuming purine-rich foods, such as red meat, seafood, and organ meats, can contribute to elevated uric acid levels.
- Genetic Predisposition: Some individuals are genetically predisposed to produce higher levels of uric acid or have difficulty eliminating it from the body.
Recognizing Symptoms of Gout
Acute Joint Pain
Gout attacks are often sudden and severe, with individuals experiencing intense joint pain, typically in the big toe. The pain can be debilitating and may last for a few days to weeks.
Swelling and Redness
Affected joints become swollen, tender to the touch, and may exhibit redness and warmth. The inflammation is a result of the body's immune response to the presence of uric acid crystals.
Limited Range of Motion
During a gout attack, individuals may experience a limited range of motion in the affected joint due to pain and swelling.
Diagnosing Gout
Clinical Examination
Healthcare professionals conduct a thorough clinical examination, assessing the affected joint for signs of inflammation, tenderness, and the characteristic appearance of gout.
Joint Aspiration
Aspiration of fluid from the affected joint allows for the examination of uric acid crystals under a microscope, confirming the diagnosis of gout.
Blood Tests
Blood tests, including serum uric acid levels, help identify elevated uric acid levels in the bloodstream, supporting the diagnosis of gout.
Treatment Approaches for Gout
Medications
- Nonsteroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs (NSAIDs): NSAIDs, such as ibuprofen, help relieve pain and reduce inflammation during gout attacks.
- Colchicine: This medication is effective in managing gout symptoms and preventing recurrent attacks.
- Uric Acid-Lowering Medications: Allopurinol and febuxostat are prescribed to lower uric acid levels and prevent future gout attacks.
Lifestyle Modifications
Dietary Changes:
- Low-Purine Diet: Limiting the intake of purine-rich foods, such as red meat, seafood, and organ meats.
- Hydration: Adequate fluid intake helps flush out excess uric acid from the body.
Weight Management:
Maintaining a healthy weight reduces the risk of gout and helps manage existing symptoms.
Alcohol Moderation:
Limiting alcohol consumption, especially beer and spirits, can decrease the likelihood of gout flare-ups.
Living with Gout
Flare-Up Management
During gout attacks, individuals are advised to rest, elevate the affected joint, and apply ice to reduce swelling. Medications prescribed by healthcare professionals should be taken as directed.
Long-Term Management
Adopting a holistic approach to gout management involves ongoing medication adherence, dietary modifications, and regular check-ups with healthcare providers.
Preventing Gout Flare-Ups
Medication Adherence
Consistent use of prescribed medications, especially uric acid-lowering medications, is crucial in preventing recurrent gout attacks.
Dietary Choices
Continued adherence to a low-purine diet, maintaining hydration, and moderating alcohol intake contribute to preventing gout flare-ups.
Regular Exercise
Engaging in regular, low-impact exercise helps maintain a healthy weight and supports overall joint health.
Emotional and Psychological Impact
Coping Strategies
Gout can impact an individual's quality of life. Implementing coping strategies, seeking support from healthcare professionals, and connecting with support groups contribute to overall well-being.
Education and Awareness
Educating oneself about gout and its management empowers individuals to actively participate in their care and make informed lifestyle choices.
Seeking Professional Guidance
Rheumatologists and Nutritionists
Consulting with rheumatologists and nutritionists with expertise in gout ensures a comprehensive assessment and personalized treatment plan. Regular follow-ups are essential for ongoing management.
Physical Therapists
Engaging with physical therapists can provide tailored exercise programs to support joint health and mobility.
Conclusion
In conclusion, gout is a manageable condition that requires a multifaceted approach involving medication adherence, lifestyle modifications, and ongoing healthcare support. By understanding the causes, recognizing symptoms, and adopting appropriate treatment strategies, individuals can effectively navigate the challenges posed by gout. Through a combination of medication, dietary changes, weight management, and regular exercise, individuals with gout can achieve optimal control of their symptoms, minimize flare-ups, and lead active, fulfilling lives. Proactive measures, coupled with awareness and education, form the cornerstone of a comprehensive approach to preventing and managing gout.
Disclaimer:
The information on this website is provided for educational and information purposes only and is not medical advice. Always consult with a licensed medical provider and follow their recommendations regardless of what you read on this website. If you think you are having a medical emergency, dial 911 or go to the nearest emergency room. Links to other third-party websites are provided for your convenience only. If you decide to access any of the third-party websites, you do so entirely at your own risk and subject to the terms of use for those websites. Neither Sheldon H. Nadal, D.P.M., nor any contributor to this website, makes any representation, express or implied, regarding the information provided on this website or any information you may access on a third-party website using a link. Use of this website does not establish a doctor-patient relationship. If you would like to request an appointment with a health care provider, please call our office at (416) 486-9917.

